CEREBRAL CORTEX

Pastries - $4
Butter Croissant - $2.5
Coffee/Tea - $1
Fresh Juice - $2
Neocortical Layers

Modified from Ranson, S.W. and Clark, S.L. 1959 Anatomy of the Nervous System, 10th ed. Philadelphia, W.B. Saunders Co.
Link: https://vanat.ahc.umn.edu/brain18/pages/neocorticalLayers.html
Layer 1: Molecular Layer
Cell sparse, lies against pia mater. Plays an important role in development.
Cajal-Ratzius neurons do inside-out layering by releasing reelin to call neurons up.
Layer 2: External Granular Layer
Small cell bodies.
Receive inputs from other cortical layers.
Layer 3: External Pyramidal Layer
Send outputs to other cortical layers.
Layer 4: Internal Granular Layer
Receives inputs from the thalamus.
Layer 5: Internal Pyramidal Layer
Send outputs to subcortical areas; corticospinal and corticobulbar fibers project from this region through the internal capsule. The largest neurons are in this region.
Layer 6: Multiform Layer
White matter.
Send fibers to the thalamus; these fibers will project through the internal capsule.
LOBES OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX

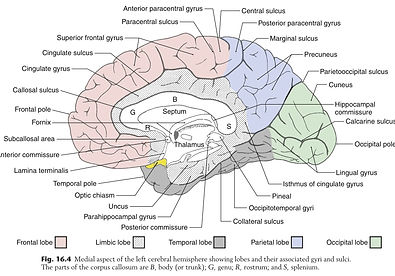

Haines, D. E., Mihailoff, G.A. (2018). Fundamental Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications (5th ed.). Elsevier, Inc.
BASAL GANGLIA (NUCLEI)

HIPPOCAMPUS




